3-Hydroxypropenal ("malonaldehyde")
 | |
|---|---|
| Species tag | 072504 |
| Version | 2* |
| Date of Entry | May 2024 |
| Contributor | H. S. P. Müller |
|
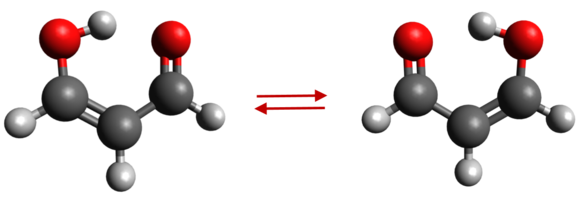
Note: Even though
the molecule is better known as malonaldehyde, it is
much better described as 3-hydroxypropenal. The enol
form of the molecule is greatly favored because it
permits intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The molecule
has a double minimum potential, and tunneling leads
to splitting. | |
| Lines Listed | 73740 |
| Frequency / GHz | < 1500 |
| Max. J | 138 |
| log STR0 | -8.3 |
| log STR1 | -6.7 |
| Isotope Corr. | |
| Egy / (cm–1) | 0.0 / 21.583 |
| µa / D | 0.36 |
| µb / D | 2.58 |
| µc / D | |
| A / MHz | 9839.956 |
| B / MHz | 5185.627 |
| C / MHz | 3393.807 |
| Q(300.0) | 253743.6527 |
| Q(225.0) | 162070.0020 |
| Q(150.0) | 85432.7456 |
| Q(75.00) | 27656.1634 |
| Q(37.50) | 8456.4390 |
| Q(18.75) | 2478.4133 |
| Q(9.375) | 764.0464 |
| Q(5.000) | 289.0967 |
| Q(2.725) | 117.1526 |
| detected in ISM/CSM | yes |